In the quest of capturing a segment of the AI market, companies are not only bringing their own Large Language Models but are also refining them in order to decrease their probablity of hallucination.
Often times, LLMs produce inaccurate answers which are not factually true. Such answers are can be false, fabricated or even inconsistent with the training data.
In order to mitigate the above problem, Google has bring in DataGemma. It is an open source initiative by the leading search engine company that will connect the LLMs to the library of real-world data available on Datacommons.org
For those of you who are not aware, Datacommons.org is owned by Google and collects all sorts of information from highly credible sources. It is a publicly available knowledge graph containing over 250 billion points of data points across hundreds of thousands of statistical variables. Users can interact with the database in conversational style as it is AI-powered.
Methods to handle Hallucination
In order to encourage factual, accurate responses through LLM every time, DataGemma will surf the Datacommons library so that instances of hallucination can be reduced to zero. Google claims that it has observed noticeable claims by utlizing DataGemma for its LLMs.
Basically Google has listed down two approaches that DataGemma will utilize. RIG (Retrieval-Interleaved Generation) and RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation).
With the help of RIG (Retrieval-Interleaved Generation), the data that is about to be produced in an answer will be fact-checked with the data available on Datacommons.org so that there will be minimal chance of producing inaccurate data in the output.
The other method is RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) which allows for more collection of relevant data in order to support the answer.
Google shared an example on their blog post of how RIG and RAG methods can help LLMs to produce factually correct answers.
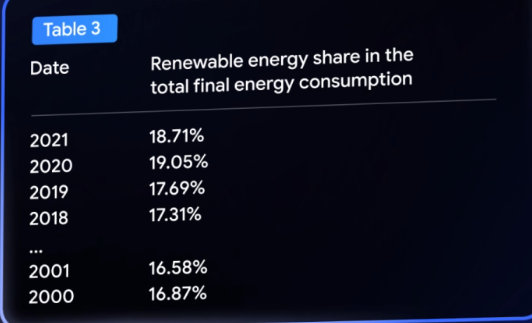
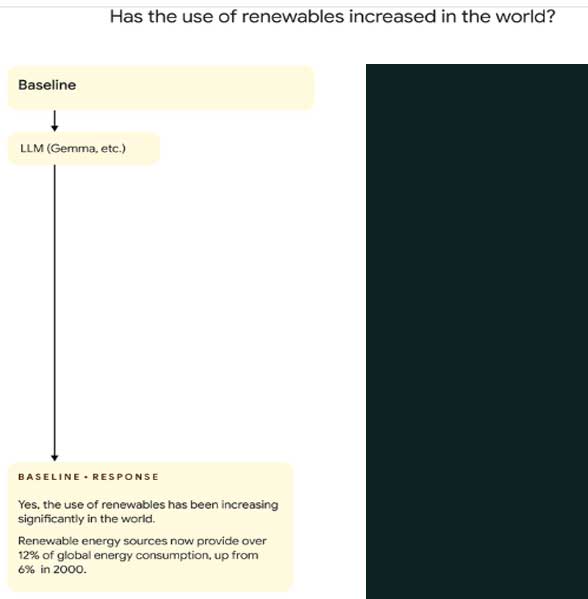
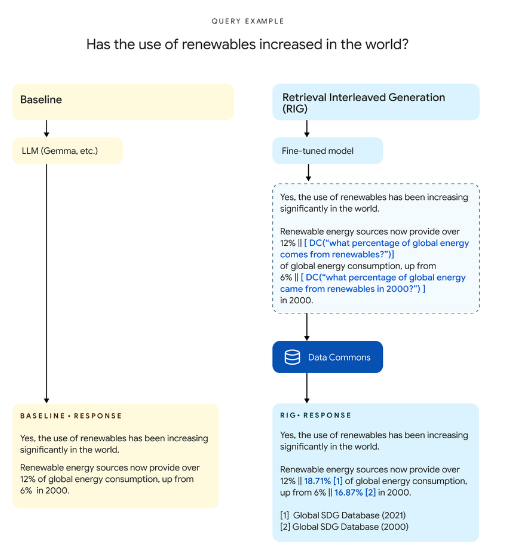
In one of the example, when a user asks “Has the use of Renewables increased in the world”, the RIG method fact-checks the data in the answer from the information available on Datacommons (which contains data from credible sources). Upon checking, the correct data is produced.
Initially the LLM answered that renewable sources accounts for 12% of global energy consumption, up from 6%.

However, the RIG method checks this data from the data available on the Datacommons.org and rectifies it later in the answer as shown below.
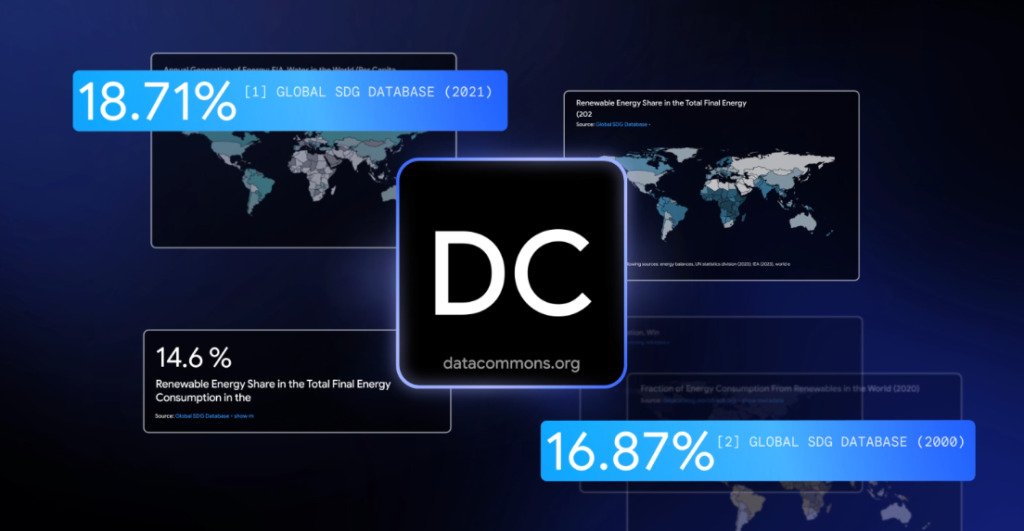
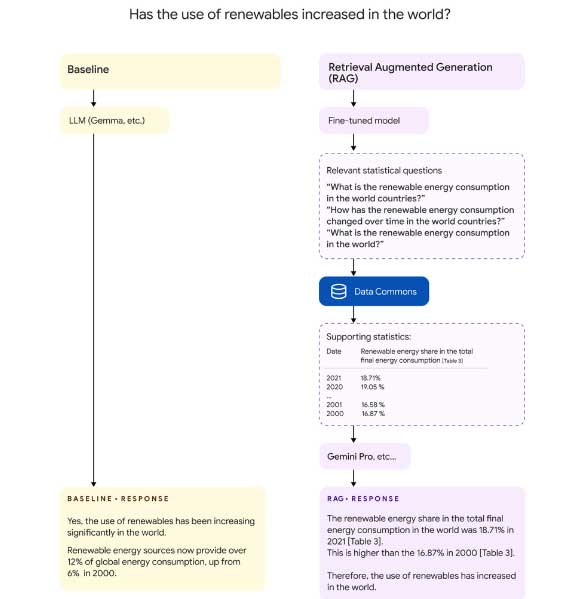
When it comes to RAG method, DataGemma will look to provide more “comprehensive and informative outputs” as stated by Google.
For e.g. in the previous example of “Has the use of Renewables increased in the world”, the RAG method would instead produce comprehensive data in order to support the answer as shown in below image where it has shown the increased in renewable energy consumption through from 2018 – 2021 and has compared it with data of 2000 – 2001.